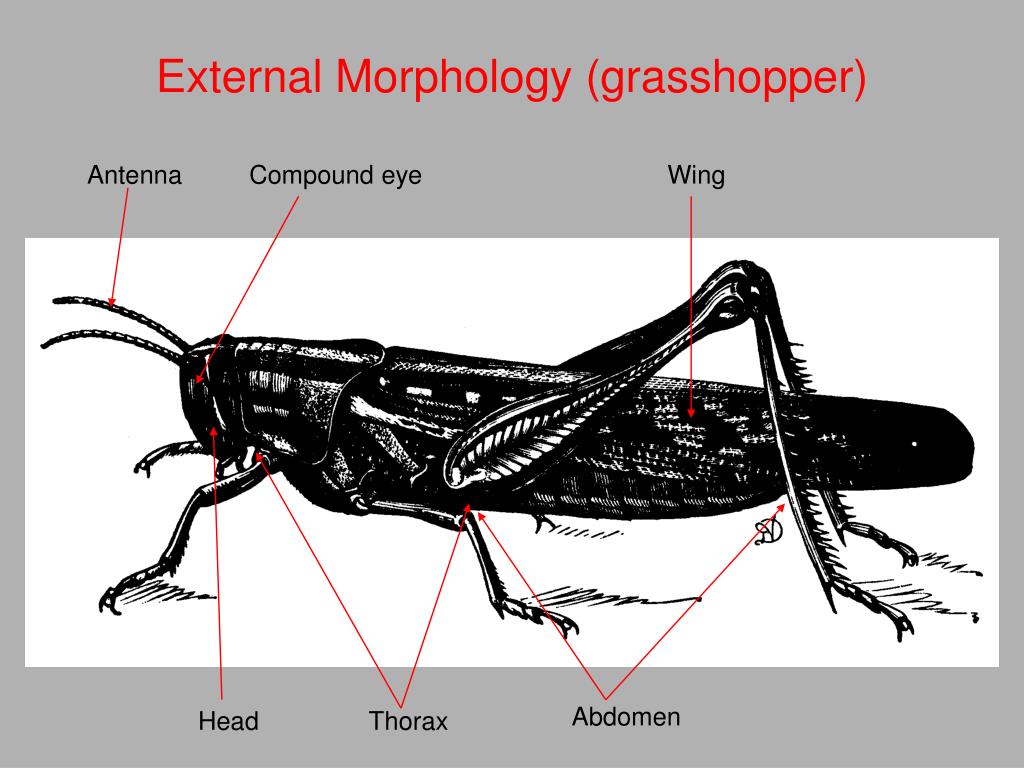
Insect Antennae Morphology . — in this study, the fine morphology of antennae as well as the typology, morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla were. This socket allows the insect to move and rotate the antenna easily. All insect antennae have three basic parts: It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement. — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. The next segment is the pedicel. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket.
from www.slideserve.com
This socket allows the insect to move and rotate the antenna easily. — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. The next segment is the pedicel. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. — in this study, the fine morphology of antennae as well as the typology, morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla were. All insect antennae have three basic parts: The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement.
PPT Entomology 462 Insect Morphology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID357920
Insect Antennae Morphology — in this study, the fine morphology of antennae as well as the typology, morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla were. It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. All insect antennae have three basic parts: — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. The next segment is the pedicel. This socket allows the insect to move and rotate the antenna easily. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. — in this study, the fine morphology of antennae as well as the typology, morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla were.
From www.thoughtco.com
The 13 Forms of Insect Antennae Insect Antennae Morphology — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. —. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.insectsexplained.com
External morphology of insects Insect Antennae Morphology — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. — in this study, the fine morphology of antennae as well as the typology, morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla were. This socket allows. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Entomology 462 Insect Morphology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID357920 Insect Antennae Morphology The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. . Insect Antennae Morphology.
From mobie21mov.blogspot.com
[Download 23+] Animals That Have Antennae Two Examples Insect Antennae Morphology This socket allows the insect to move and rotate the antenna easily. All insect antennae have three basic parts: — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement. — in this study, the. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Musca (house fly) PowerPoint Presentation ID1896926 Insect Antennae Morphology All insect antennae have three basic parts: This socket allows the insect to move and rotate the antenna easily. The next segment is the pedicel. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement.. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From whatbugisthat.com
Bee Antennae, An Amazing Sensory Super Highway WhatBugIsThat Insect Antennae Morphology It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement. — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. The next segment is the pedicel. — in this study, the fine. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.pinterest.com
Aristate antennae, common in flies Study materials, Antenna, Entomology Insect Antennae Morphology It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. All insect antennae have three basic parts: The. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.insectsexplained.com
External morphology of insects Insect Antennae Morphology — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. The scape is the first segment and. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From kids.britannica.com
insect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help Insect Antennae Morphology — in this study, the fine morphology of antennae as well as the typology, morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla were. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. The next segment is the pedicel. — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Insect Antennal Morphology The Evolution of Diverse Solutions to Odorant Perception Insect Antennae Morphology The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. The next segment is the pedicel. — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. All. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From encyclopedia.pub
Antenna Encyclopedia MDPI Insect Antennae Morphology The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. All insect antennae have three basic parts: — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement. The next segment is the pedicel.. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.rawpixel.com
Antennae from Moths and butterflies Free Photo rawpixel Insect Antennae Morphology — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. This socket allows the insect to move and rotate the antenna easily. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. All insect antennae have three basic parts: — as the major olfactory. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.mdpi.com
Insects Free FullText Functional Morphology of the Antennae and Sensilla of Coeloides Insect Antennae Morphology — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. This socket allows the insect to move and rotate the antenna easily. — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. All insect antennae have three basic parts: The. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT External Anatomy II Lecture 11 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2123460 Insect Antennae Morphology The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. — in this study, the fine morphology of antennae as well as the typology, morphology and distribution of. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From entomology.unl.edu
Basic Insect Morphology Science Literacy and Outreach University of NebraskaLincoln Insect Antennae Morphology All insect antennae have three basic parts: — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae,. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From blogs.evergreen.edu
Types of Antennae Colton's Field Study Insect Antennae Morphology — as the major olfactory sensory organ, antennae are crucial for insects to locate food resources, mating partners and oviposition sites, as. The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. This. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From entomology.unl.edu
Basic Insect Morphology Science Literacy and Outreach Nebraska Insect Antennae Morphology The scape is the first segment and is attached to the head of the insect inside a socket. — insects detect these odors with receptors mostly located on the antennae, and the diverse shapes and. The next segment is the pedicel. This socket allows the insect to move and rotate the antenna easily. — as the major olfactory. Insect Antennae Morphology.
From dxowcjnmt.blob.core.windows.net
How Do Insect Antennae Work at Angeline Taylor blog Insect Antennae Morphology — an elongate, cylindrical morphology, probably the ancestral condition for insect antennae, is found in fossil. It contains muscle connections allowing the insect greater control over antennal movement. All insect antennae have three basic parts: — in this study, the fine morphology of antennae as well as the typology, morphology and distribution of antennal sensilla were. —. Insect Antennae Morphology.